How Do I Register 10.x Esri
As an ArcGIS Server administrator or a publisher in your organization, you have the pick to register your on-premises data stores and deject stores. In doing then, yous are registering information folders, databases, and geodatabases with the ArcGIS Server site and so that services y'all publish can reference the data in those folders, databases, and geodatabases. Data registration provides ArcGIS Server a list of locations to access. Data registration also helps ArcGIS Server adjust data paths when publishing beyond machines.
Suppose you're an ArcGIS Server administrator and yous accept a department of GIS analysts who publish services to your ArcGIS Server site from dissimilar client machines. Using tools in ArcMap, ArcGIS Pro, or ArcGIS Server Managing director, yous tin register a set of canonical information store locations with the site and communicate these locations to your analysts. Publishers can also register canonical folders, databases, enterprise or workgroup geodatabases, deject stores, and raster stores with the site. Registering these data stores with the ArcGIS Server site decreases the number of incidents where your analysts meet permissions problems and cannot publish. The publisher tin can create services that reference the data in the registered data stores.
Data sources you lot can annals
The side by side five sections describe the information stores that publishers and ArcGIS Server administrators can register with an ArcGIS Server site.
If your data locations change, add more registered data locations.
Databases
You tin annals any database management organisation that ArcGIS supports past referencing the database connexion file (.sde). The database you lot connect to can contain a geodatabase, but it doesn't have to.
If you use a database-authenticated user to connect, the user account data must be saved with the .sde file, and that user must take the necessary privileges to the data to exist published. For case, if you publish a feature service that y'all want people to use for updating and adding features, the user saved with the registered connection file must have update and create privileges on the data in the database.
If you lot use operating system authentication, you must add the ArcGIS Server account to the database and grant it the privileges necessary to admission the information.
If the database you register contains a versioned geodatabase, ArcGIS Server accesses the version of that data present in the geodatabase version yous set for the connexion file. If you lot desire ArcGIS Server to access dissimilar versions, you must annals divide connection files to connect to these geodatabase versions. For instance, y'all may need to annals one connection file that accesses the Default geodatabase version and one that accesses a child version.
You can also annals a database with the ArcGIS Server site by referencing an OLE DB connexion (an .odc file). OLE DB connections provide uniform access to information from a variety of database sources only are nonspatial connections. You tin can register these files in ArcGIS Server Director or ArcMap.
Even if you annals the OLE DB connection from some other ArcGIS application, data from OLE DB connections is always copied to the server and converted to file geodatabase tables when publishing from ArcGIS Pro to ane of your portal'south federated servers.
Folders
You can register local and shared operating arrangement folders with the ArcGIS Server site that includes data files you want to publish. These folders can contain shapefiles, file geodatabases, locator files, imagery (raster) files, and big data files.
When you register a folder, its subfolders are likewise registered. Practice not annals an entire drive with ArcGIS Server due to security considerations.
Big data file shares
Big data file shares are shared operating system folders, Hadoop Distributed File Systems (HDFS), Apache Hive, or deject stores containing collections of delimited files or shapefiles used as input for GeoAnalytics Tools.
To employ a cloud store every bit a big data file share, you must starting time register the cloud shop. Big data file shares support Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) buckets, Microsoft Azure Blob storage containers, and Microsoft Azure Data Lake Stores.
See Get started with big data file shares for information on registering big information file shares.
Raster stores
Raster stores are an output data shop; they comprise the imagery layers created when you lot run raster assay tools. Raster stores can be either a file share or a cloud store.
To apply a cloud store equally a raster store, you lot must first register the cloud store. Raster stores support Amazon S3 buckets and Azure Hulk storage. At x.half-dozen.ane, y'all tin can also use Alibaba Cloud Object Storage Service (OSS).
Run into Configure and deploy ArcGIS Enterprise for raster analytics in the Portal for ArcGIS administrator guide for information on registering a raster shop.
Cloud stores
You can register an Amazon S3 bucket or Microsoft Azure Blob storage container to utilise every bit a raster store, big information file share, or to store map and prototype caches. At x.6.1, you can annals an Alibaba OSS every bit a deject store for map and image service caches or to utilize as a raster store. Also at x.6.1, you tin can register a Microsoft Azure Information Lake store every bit a deject store to be used for big data file shares
You should only employ a cloud shop for map and epitome service caches if your ArcGIS Server site is running on that same deject platform. For example, only utilize Azure Blob storage for map and image service caches if your ArcGIS GIS Server and ArcGIS Image Server sites are running on Microsoft Azure.
Before registering data
Registering your information does not grant the ArcGIS Server site permissions to access your information. Before registering your information, you'll need to ensure that the ArcGIS Server account has at least read permissions to the data stored in folders, workgroup geodatabases, or in databases or enterprise geodatabases that are accessed using operating arrangement authentication. For databases or enterprise geodatabases that are accessed using database authenticated users, that user must be granted permissions to the data. To acquire more nearly this procedure, see Make your information accessible to ArcGIS Server.
If you lot'll exist registering an enterprise geodatabase or database (a .sde or .odc file) with the ArcGIS Server site, you'll also need to ensure that the 64-bit version of the database'southward customer software is installed on each ArcGIS Server machine in your site. For example, if you plan to register a SQL Server database, you must install SQL Server client on each ArcGIS Server machine in your site. Keep in mind that once you've installed the client software, you lot'll demand to restart the ArcGIS Server service.
The following links describe the customer software needed for each database, how to grant the ArcGIS Server account data admission privileges, and how to connect to the database:
- Register ALTIBASE with ArcGIS Server
- Register a Dameng database with ArcGIS Server
- Register a Db2 database with ArcGIS Server
- Register a Netezza database with ArcGIS Server
- Annals an Oracle database with ArcGIS Server
- Register a PostgreSQL database with ArcGIS Server
- Register SAP HANA with ArcGIS Server
- Annals a SQL Server database with ArcGIS Server
- Annals a Teradata database with ArcGIS Server
- Register a workgroup geodatabase with ArcGIS Server
You cannot annals Informix databases or Db2 on z/OS databases with an ArcGIS Server site. Instead, create a service definition file that references the information in the database and publish the service definition file.
Scenarios for registering your data
Before registering your data, examine the following scenarios and consider how your workflows relate:
A) The publisher'southward motorcar and the ArcGIS Server site reference the same database
If the publisher's automobile and the ArcGIS Server site will reference the data in the same database, workgroup geodatabase, or enterprise geodatabase, import the publisher'south database connectedness and set the ArcGIS Server site's database connectedness to Same as publisher's connectedness when registering your data.
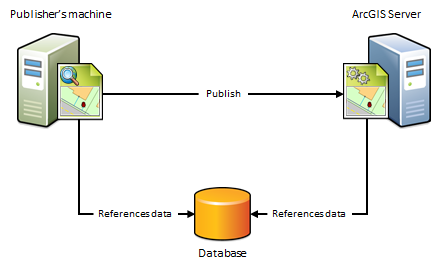
When to utilise this scenario
Utilise this scenario if y'all want to avoid having a copy of the data placed on the ArcGIS Server machines. For example, suppose yous want to publish a map service to ArcGIS Server from ArcMap or publish a map epitome layer to i of your portal's federated servers from ArcGIS Pro using data from an on-premises enterprise geodatabase. To avert having a copy of the data referenced past your map document placed in a folder on one of the ArcGIS Server machines, import the publisher's database connexion and set the ArcGIS Server site'southward database connection to Same every bit publisher'due south connectedness. After you publish, the map document continues to reference the data stored in your enterprise geodatabase.
When not to use this scenario
- If your data resides in a file geodatabase or file directory. Instead, utilise the next scenario.
- If you want to maintain a split copy of the information in your enterprise geodatabase for web use.
B) The publisher'south machine and the ArcGIS Server site reference the same binder
If the publisher'southward machine and the ArcGIS Server site will reference data in the same folder, specify the publisher's folder path and set the ArcGIS Server site'southward folder path to Same every bit publisher's path when registering your data. This scenario is just like the previous one, except it uses folders, not databases.
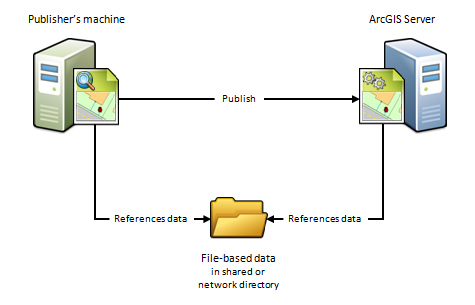
When to use this scenario
Use this scenario if you desire to avoid having a copy of the data placed on one of the ArcGIS Server machines. For instance, suppose yous want to publish a geoprocessing service to ArcGIS Server using data from a network directory. To avoid having a re-create of the geoprocessing service's data copied to 1 of the ArcGIS Server machines, specify the publisher'due south folder path and gear up the ArcGIS Server site's folder path to Aforementioned as publisher's path. Afterward you publish, the geoprocessing service continues to reference the geoprocessing model, inputs, outputs, scripts, and project data stored in your network directory.
This scenario is besides beneficial if y'all have a Linux-based ArcGIS Server site that manages all of your data and you've set up Samba to permit file sharing between Windows and Linux. For instance, if you want to publish a map document that references the data on your Linux auto, register the Samba directory (\\net\data) as the publisher's folder and register the Linux directory (/net/data) as the ArcGIS Server site'due south folder. When you publish, the map document is automatically modified to reference the directory on the Linux auto.
When not to employ this scenario
- If your data resides in a database. Instead, apply the preceding scenario.
- If you lot desire to publish feature or WFS-T services.
C) The publisher's car and ArcGIS Server site reference unlike geodatabases and the data is not static
Because of firewalls, differences between computing platforms, or the desire to keep a dissever copy of the information for spider web use, the publisher and ArcGIS Server site may each reference the aforementioned data in different geodatabases. To register your data using this scenario, you'll demand to import both the connection to the publisher'southward database and the connection to the ArcGIS Server site's geodatabase.
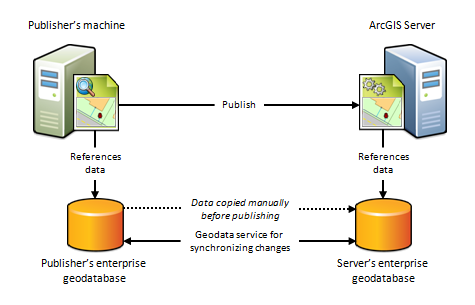
When to use this scenario
Use this scenario if you desire to maintain a separate copy of the data in your on-premises enterprise geodatabase for web use. In this example, you're responsible for making sure a copy of the information in your publisher's geodatabase exists in the ArcGIS Server site'southward geodatabase. This scenario can just exist used with enterprise geodatabases; not databases.
To allow you to replicate information so both the publisher and the ArcGIS Server site take access to changes the information, check Create geodata service for server database when registering your enterprise geodatabases in ArcMap. Selecting this option automatically creates a geodata service that you lot tin use to manually ship a replica of the data in the publisher's geodatabase to the ArcGIS Server site's geodatabase.
Y'all tin can also use the geodata service to synchronize the enterprise geodatabases, thereby ensuring that whatever subsequent changes made to the publisher'south database are reflected in the ArcGIS Server site'south geodatabase. This is particularly advantageous in deject deployments every bit information technology does not require someone to log in to the cloud machine and arrange for the data transfer.
This scenario is besides well suited for publishing characteristic services to ArcGIS Server sites on-premises or in the cloud. For case, if you publish a feature service using this scenario, edits made on-premises could be pushed to the ArcGIS Server site's geodatabase, thereby condign available to end users of your characteristic service. Conversely, if web editors change any features in the ArcGIS Server site's geodatabase, the edits tin can be synchronized with the publisher's geodatabase.
When not to use this scenario
- If your information resides in a file geodatabase or file directory. Instead, use scenario D.
- If your data resides in a database (one that does not incorporate a geodatabase). Instead utilize scenario A.
- If you practise not desire to maintain a separate copy of your geodatabase on the server.
- If you are publishing to one of your portal'due south federated servers from ArcGIS Pro.
- The published data is static. In that example, you don't demand to synchronize changes from the publishers geodatabase to the ArcGIS Server site'southward geodatabase. In that example, yous can utilise a managed database scenario without replication.
D) The publisher's auto and the ArcGIS Server site reference unlike folders
Because of firewalls, differences betwixt calculating platforms, or the want to continue a separate copy of the data for spider web use, the publisher and the server may each reference copies of the aforementioned information in their own data folder. To annals your data using this scenario, you'll need to enter the path to both the publisher's binder and the server's folder.
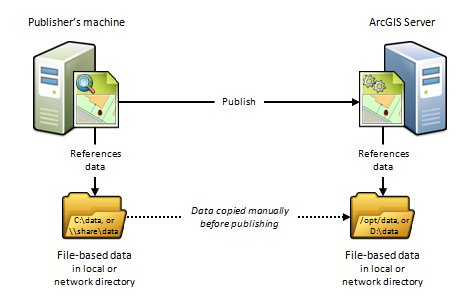
When to use this scenario
This scenario is useful for Linux deployments, deject deployments, or whatever deployment where you want publishers and web users to work with dissever copies of the data.
For example, if you want to publish a map service from ArcMap to a Linux-based ArcGIS Serversite, you could create an identical copy of your map certificate'south information and place the data on the Linux-based server. After y'all register both directories with the server and publish, the map document is automatically modified to reference the folder on the Linux-based server.
This scenario is beneficial if you are publishing to a cloud-based server such as ArcGIS Enterprise on Amazon Spider web Services. For example, y'all tin can re-create your on-premises data and place information technology in any directory you want to in the cloud. When you publish, the information paths are automatically modified to reference the directory on the cloud server. The disadvantage of this approach is that it requires someone to log in to the cloud machine and arrange for the data transfer to the cloud (which could be performed through FTP, remote desktop copy and paste, or other supported data transfer methods).
When non to employ this scenario
- If your data resides in an enterprise geodatabase, use scenario C instead.
- If your information resides in a database, utilize scenario A instead.
- If y'all do non want to maintain a separate re-create of your data on the server.
- If y'all are publishing to one of your portal'due south federated servers from ArcGIS Pro.
East) The publisher's machine and ArcGIS Server site reference different geodatabases
This scenario is similar to scenario C simply, in this scenario, data is not synchronized between the two geodatabases. This is useful as a method to movement feature data from your on-premises enterprise geodatabase to an enterprise geodatabase in the cloud.
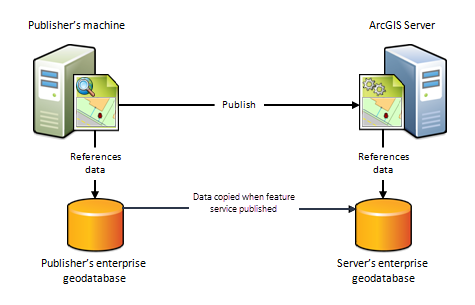
When to utilise this scenario
Utilise this scenario equally a way to motility feature information to the cloud. This scenario requires the following:
- Both the on-premises data source and the data store in the cloud must exist enterprise geodatabases.
- The enterprise geodatabase in the cloud must be registered as the managed database for a stand up-alone or federated ArcGIS Server site.
- The publisher must apply ArcMap to publish feature services to the stand up-alone or federated ArcGIS Server site in the deject.
When not to use this scenario
- If your data resides in a file geodatabase or file directory.
- If your data resides in a database (one that does not contain a geodatabase).
- If you want to synchronize information changes between the publisher's and the ArcGIS Server site'due south geodatabase, employ scenario C.
F) The publisher's machine references local map or image information and the ArcGIS Server site references a deject storage location
If your ArcGIS GIS Server site or ArcGIS Image Server site is running in the cloud and you want to store map or prototype service caches in the cloud too, provide connection and authentication information for your cloud provider before publishing. When y'all publish cached map or epitome services, the caches will reside in your registered cloud store.
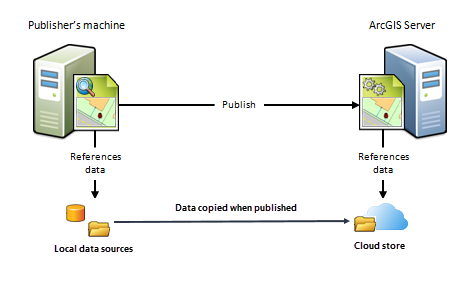
When to use this scenario
Employ this scenario if your ArcGIS Server site is running on AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Alibaba and yous want your map or paradigm services to reference caches stored in an Amazon S3 bucket, Azure Blob storage container, or Alibaba saucepan respectively.
When not to apply this scenario
- Your ArcGIS Server site is not running in the cloud.
How to register your data with ArcGIS Server
You can register your data folders, databases, and deject locations with ArcGIS Server using ArcGIS Server Managing director, ArcMap, or ArcGIS Pro. For full instructions, encounter the following:
- Register your data with ArcGIS Server using Managing director
- Register your data with ArcGIS Server using ArcGIS Desktop
Considerations when unregistering data stores
Yous should not unregister a data store if existing services contain data from the data store.
If yous practice unregister a information store from your ArcGIS Server site, and that data store is used to populate existing services, yous may still be able to view the services depending on the type of data store that was used. Keep the following limitations in mind when y'all unregister a information store:
- For registered and managed databases, you can still view the data in the services they populate. However, if the password stored with the data store changes, you cannot update your services to apply the new password. At that point, the services will no longer office, and you will have to annals the database that contains the service data and republish the services.
- For registered and managed databases, any new ArcGIS Server machines you add to your cluster will not recognize services if their source data shop is no longer registered with the ArcGIS Server site. You will have to register the database that contains the service data and republish the services to permit the new machines to recognize the services.
- You should not unregister ArcGIS Data Shop relational, tile enshroud, and spatiotemporal big data stores from the hosting server site, even though it is possible to do so in ArcGIS Server Managing director. If you unregister these data stores from Managing director, the services they populate will no longer part.
If y'all or a publisher in your system accidentally unregisters an ArcGIS Information Shop item from inside ArcGIS Server Manager (or unregisters a relational data store from inside ArcMap), y'all must reconfigure the ArcGIS Data Shop with the same ArcGIS Server site to get your services to office once again.
Feedback on this topic?
How Do I Register 10.x Esri,
Source: https://enterprise.arcgis.com/en/server/10.6/publish-services/windows/overview-register-data-with-arcgis-server.htm
Posted by: becklonot1936.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Do I Register 10.x Esri"
Post a Comment